Arsenorribosa sulfato
| Arsenorribosa sulfato | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| Nombre IUPAC | ||
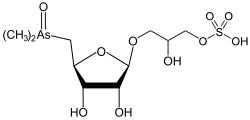
| [3-[(2R,3R,4S,5S)-5-(dimetilarsorilmetil)-3,4-dihidroxioxolan-2-il]oxi-2-hidroxipropil] hidrógeno sulfato | ||
| General | ||
| Otros nombres | Arsenoazúcar sulfato | |
| Fórmula molecular | C10H21AsO10S | |
| Identificadores | ||
| PubChem | 189292 | |
| Propiedades físicas | ||
| Masa molar | 408,258 g/mol | |
| Valores en el SI y en condiciones estándar (25 ℃ y 1 atm), salvo que se indique lo contrario. | ||
La arsenorribosa sulfato o arsenoazúcar fosfato es un oxo arsenoazúcar dimetilado que tiene un grupo sulfato de glicerol unido al carbono 1 del anillo ribosídico.
Se identificó por primera vez en 1982 en el bivalvo Tridacna maxima,[1] y es el arsenosazúcar más común junto con el glicerol, el fosfato y el sulfonato[2] (particularmente en el alga parda Hizikia fusiforme, donde se ha determinado que es el principal compuesto de arsénico).[3]
Entre los 4 arsenosazúcares principales, es el más ácido[4] y el más lábil cuando se extrae con hidróxido de tetrametilamonio o hidróxido de sodio.[5]
Véase también
Referencias
- ↑ Edmonds, J. S. (1982). «Isolation and crystal structure of an arsenic-containing sugar sulphate from the kidney of the giant clam, Tridacna maxima. X-Ray crystal structure of (2S)-3-[5-deoxy-5-(dimethylarsinoyl)-β-D-ribofuranosyloxy]-2-hydroxypropyl hydrogen sulphate». Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 1 (en inglés) (RSC) (0). doi:10.1039/P19820002989.
- ↑ Niegel, C. (2010). «Analytical methods for the determination of arsenosugars — A review of recent trends and developments». Analytica Chimica Acta (en inglés) (Elsevier) 657 (2). doi:10.1016/j.aca.2009.10.041.
- ↑ Edmonds, J. S. (1987). «Isolation and identification of arsenic-containing ribofuranosides and inorganic arsenic from japanese edible seaweed Hizikia fusiforme». Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 1 (en inglés) (RSC) (0). doi:10.1039/P19870000577.
- ↑ Madsen, A. D. (2000). «Characterization of an algal extract by HPLC-ICP-MS and LC-electrospray MS for use in arsenosugar speciation studies». Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry (en inglés) (RSC) 15 (6). doi:10.1039/B001418O.
- ↑ Gamble, B. M. (2003). «An investigation of the chemical stability of arsenosugars in basic environments using IC-ICP-MS and IC-ESI-MS/MS». The Analyst (en inglés) (RSC) 128 (12). doi:10.1039/B306931A.